Whether you are in the hospitality, pharmaceuticals, food, or dairy industry, cold storage has become a critical part of businesses. Tightening regulations around the safety of the products and consumer demand for high-quality products with intact flavour, texture, and integrity makes it more important than ever to invest in effective cold storage solutions. In fact, the global cold storage market is expected to be valued at around USD 372 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 13.4%. Increasing demand for frozen and chilled food as well as the growth of organized retail stores will be the primary growth drivers of this sector.
So, let us understand everything you need to know about cold storage to make the right decision for your business.
What Is Cold Storage?
Cold storage can be described as a special facility or unit that is used primarily for storing temperature-sensitive, perishable products to enhance the shelf-life and avoid degradation or contamination.
When short-lived products get destroyed due to unsuitable storage conditions, it leads to big losses in the inventory and profitability. Plus, there is a health risk involved for your consumers.
Therefore, the effort should be to identify cost-effective and energy-efficient cold storage solutions based on the product type and the appropriate temperature range for their long-term storage.
Cold Storage: Industry and Applications
Cold storage has widening applications across industries.
- Retail food industry: Frozen foods including meat, poultry, seafood, dairy, fruits, and vegetables need to be maintained at a temperature of around -18°C to avoid deterioration or contamination. Depending on the duration of the storage and logistics to make the product accessible to the customers, you can choose your cold storage solutions.
- Post-harvest products: Post-harvest fresh produce, including fruits, vegetables, milk or even fish, must be stored at cooler temperatures or refrigerated to avoid ripening and degradation. Fruit and vegetables especially need a controlled atmosphere with the right amount of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, humidity, etc. to prolong their shelf-life.
- Pharmaceuticals industry: Drugs, vaccines, biologics, laboratory specimens or samples, and other pharmaceuticals need to be maintained at specified temperatures to ensure safety and integrity. Usually, the temperature requirement is between 2°C and 8°C.
- Hospitality industry: Restaurants and hotels need to keep the beverages, food ingredients, and stock items safe and ready to use. These places also keep surplus meal preps for quick serving and catering, requiring effective refrigeration solutions that keep the flavour, quality, and texture intact.
- Horticulture: Florists or suppliers also require cold storage facilities to store ornamental plants or flower stems (once they have been cut). Even seeds, spices, and dry fruits need appropriate cold storage conditions for a longer shelf-life.
How Does Cold Storage Work?
A cold storage facility or unit relies on a refrigeration system to maintain appropriate temperature conditions and primarily consists of the following components.
- Compressor: It is a significant component of a cold room and consumes maximum power. It increases the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant gas from the evaporator. With increasing pressure, the boiling point also increases and the compressor then condenses the refrigerant gas to the temperature of the condenser.
- Condenser: This component acts as a heat exchanger and removes heat from the refrigerant and the circulating water. Higher the efficiency of a condenser, better the working of a cold room.
- Evaporator: It takes heat from the storage unit or the atmosphere to keep the area cooler, vapourising the liquid refrigerant.
- Receiver: It can be primarily considered a storage area for liquid condensate. Also, the liquid refrigerant enters the expansion valve from this component for the reduction in temperature and pressure.
- Expansion valve: It is used to reduce the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant. The pressure change occurs from the receiver to the evaporator.
- Fans: The fans or blowers are used to circulate the cooler air across the cold room through the process of convection.
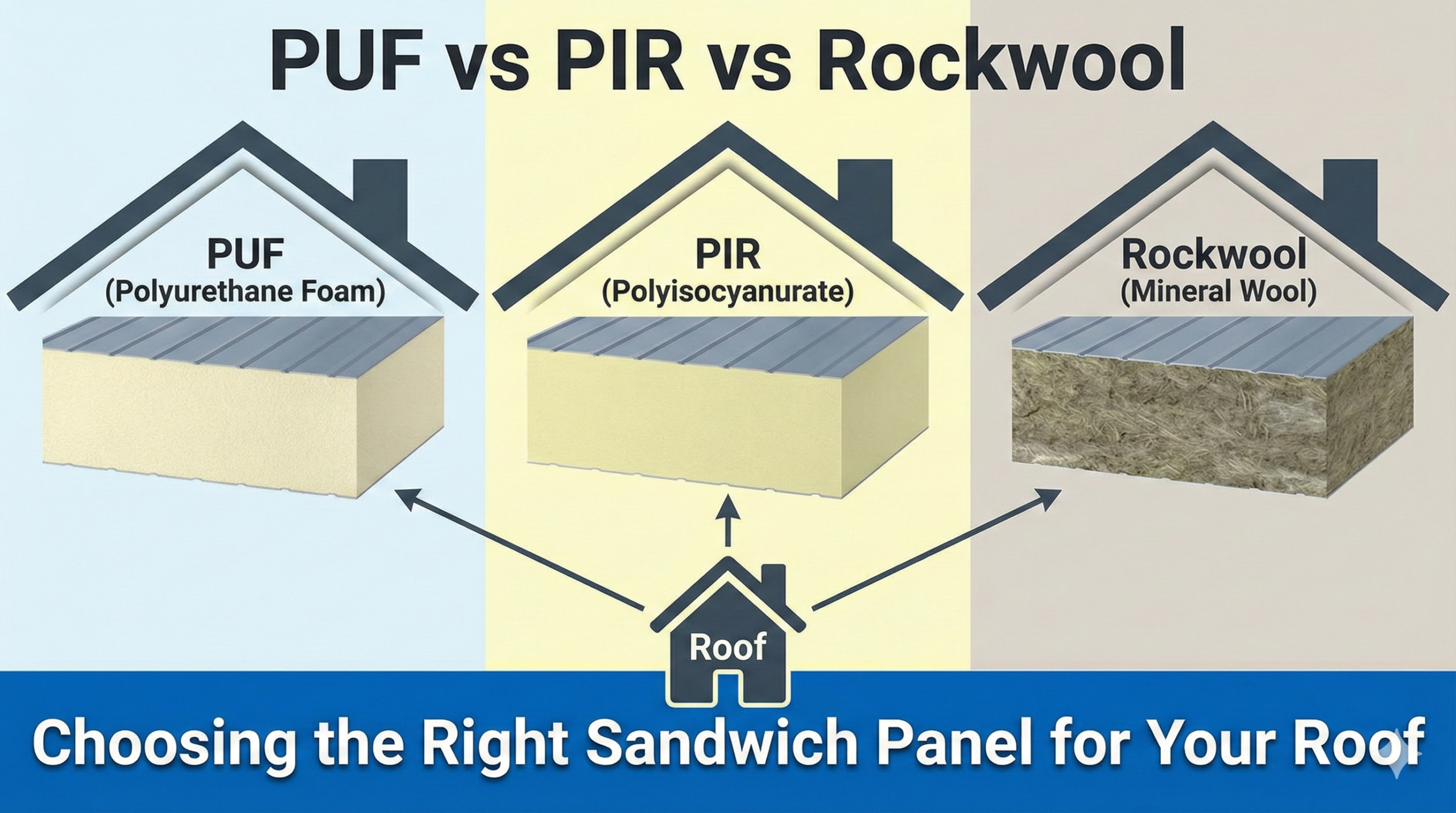
Types of Cold Storage
Depending on the product type, capacity, and storage duration, a variety of cold storage are available for businesses.
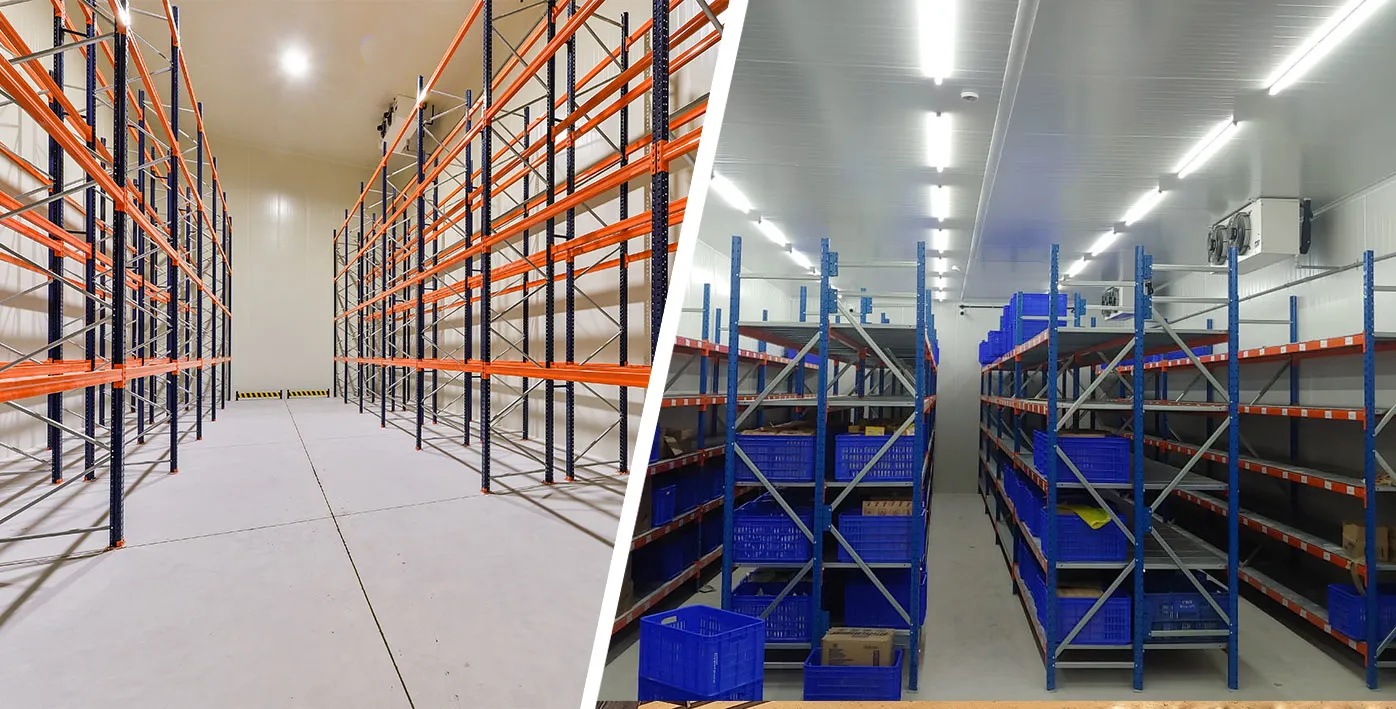
- Multi-commodity cold warehouses: These warehouses are used to store a variety of products and fresh produce that require different temperature and storage conditions. These modular warehouses are quick and easy to install. Plus, with effective racking solutions, you can maximise the space for storage.
- Walk-in chillers and freezers: Walk-in chillers (2°C to 8°C) and freezers (-18°C to -20°C) are modular cold rooms for storage of food, beverages, pharmaceutical products, etc.
- Step-in chillers and freezers: Step-in chillers and freezers are compact cold storage rooms for short-life, perishable products.
- Display cum cold rooms: These units are a combination of display and backend cold rooms and are used for packaged frozen food, beverages, dairy products etc. Display cum cold rooms find extensive usage in supermarkets, hotels, and retail chains.
- Refrigerated transportation (Reefer trucks): Reefer trucks are critical in cold supply chain logistics. Effectively supporting last-mile deliveries and long-distance transportation, reefer trucks with insulated walls can help maintain a stable temperature for a longer time. There are also eco-friendly eutectic trucks that are not only energy efficient but offer significant cost savings.
- Controlled atmosphere (CA) and modified atmosphere (MA) chambers: CA and MA chambers help store fruits, vegetables, grains, and other food items including dry fruits and spices. These units control the gaseous environment (O2, O2, N2, and ethane), so you can effectively reduce the rate of respiration, microbial growth, and enzymatic spoilage or browning.
Final Words
Cold storage finds application in various industries to prolong the shelf-life and ensure the safety, integrity, and freshness of the products. Depending on the type of the food or product, capacity, storage conditions and storage duration, your business will need to select energy-efficient and cost-effective cold storage.
Know how Rinac, a global leader in cold storage solutions and processes can help you with the perfect cold storage to improve your profitability!