Why ASRS—and why now, in India?
Land costs, power tariffs, and labour constraints are pushing Indian warehouses—especially cold stores and pharma DCs—to extract more throughput from the same footprint while tightening temperature and quality controls. ASRS (Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems) do exactly that: they condense storage into vertical cubic space, automate put-away and retrieval, and cut travel time, mispicks, and product exposure to ambient air. Recent industry coverage highlights two recurring advantages in cold storage settings: higher storage density and lower energy per pallet, because a smaller refrigerated envelope reduces thermal gains and door openings versus forklift-intensive layouts.
India’s warehousing is also digitising fast: multiple market trackers point to strong growth in warehouse automation and ASRS adoption across the next few years, driven by e-commerce, FMCG, and pharma. While individual projections vary by source, the direction is clear—automation is moving from “nice-to-have” to default for high-volume Indian facilities.
How Rinac fits: ASRS within a complete storage & envelope stack
Rinac offers ASRS as part of its broader StorEdge storage portfolio—so you can pair high-density racking and automation with the right building envelope (insulated panels, fire-rated assemblies) and cold-chain process equipment. StorEdge covers rack-/mezzanine-assisted storage, selective (single/double-deep), multi-deep drive-in, multi-deep shuttle racking, mobile racking, and ASRS, designed to EN 15512 principles for steel static storage systems. This means structural design is aligned with established rack engineering practice—a key consideration for safety and regulatory acceptance in India.
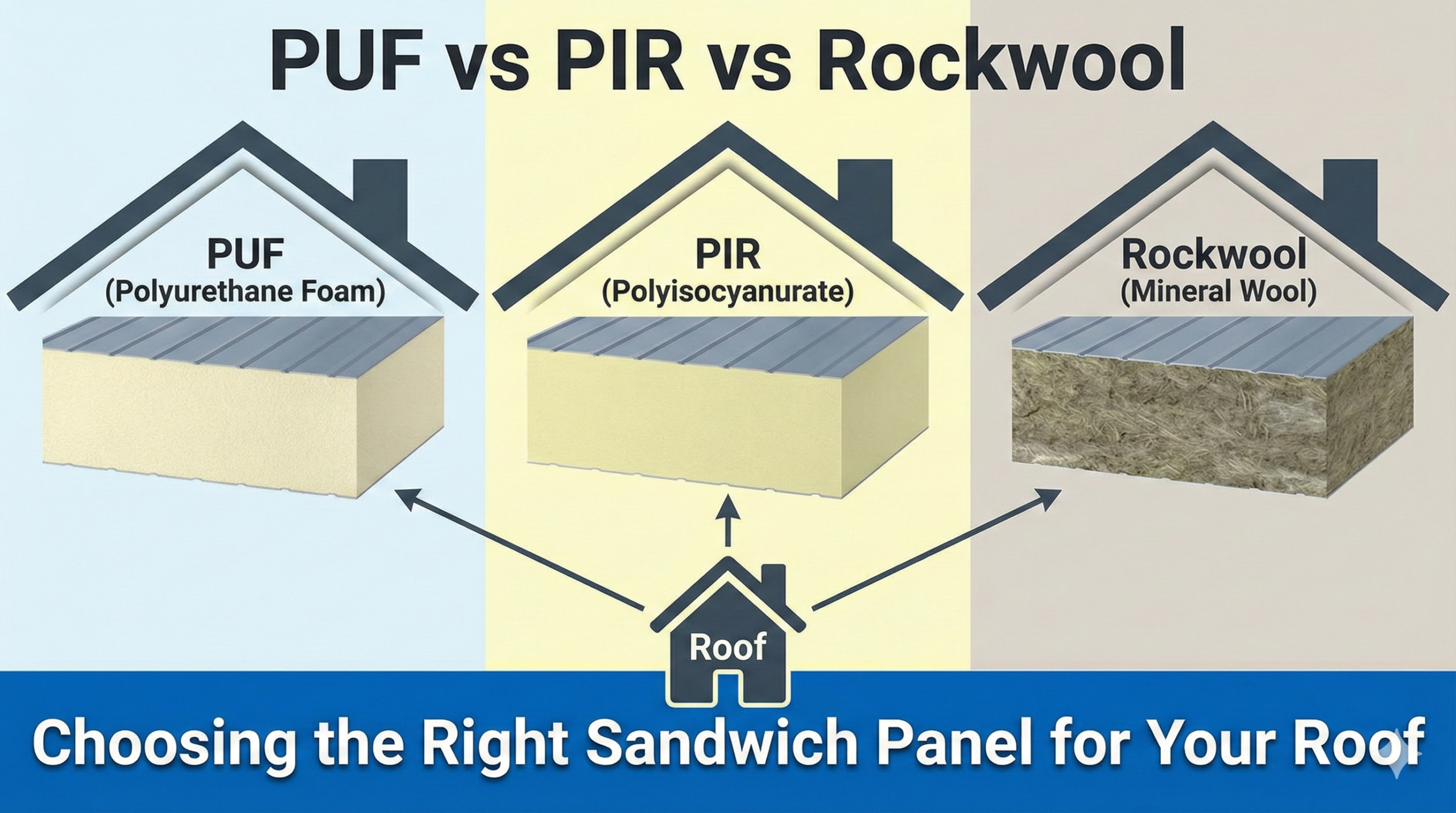
For the building shell and internal controlled spaces, Rinac supplies PUF/PIR insulated sandwich panels (InstaWall, InstaCeil, InstaRoof) and Firearmet FM-Approved PIR panels (Elastopir core) for higher fire performance in cold stores and industrial envelopes—useful when your ASRS runs inside a refrigerated or ambient warehouse that must meet rigorous fire & life-safety goals. Firearmet is listed with FM Approvals Class 4880, 4881, and 4471 and manufactured under ISO/EN 14509 quality controls.
At a glance—Rinac building & storage pieces you can mix for ASRS projects
-
StorEdge racking & automation (selective, shuttle, mobile, mezzanine, ASRS) – EN 15512 design basis.
-
PUF sandwich panels for walls/ceilings/roofs (InstaWall/InstaCeil/InstaRoof).
-
Firearmet FM-Approved PIR panels for higher fire resistance and envelope reliability.
ASRS 101: What it is and common architectures
ASRS is an integrated system of high-density racks and automated machines (cranes, shuttles, lifts) coordinated by software to store and retrieve totes, cartons, or pallets. In Indian warehouses, the most common patterns are:
- Unit-load ASRS (pallet cranes): Tall aisles with stacker cranes that deposit/collect pallets in beam locations—ideal for large pallet volumes and deep verticals.
- Shuttle-based deep-lane (pallet shuttles): Motorised shuttles carry pallets into deep channels; lifters or reach equipment feed front faces. Great for batch SKUs and high density.
- Miniload/box ASRS (case/tote cranes or shuttles): For pharma, cosmetics, or spares with tight accuracy and smaller loads.
- Mobile racking with automation: Racks ride on powered bases, creating a single movable aisle to maximise density; can be paired with guided picking or AGVs.
Where they shine: cold stores, pharma DCs, e-grocery, dairy, seafood, seeds & agri-inputs, and high-mix spares—anywhere density, traceability, and temperature/quality controls matter.
The business case: density, energy, labour, and service level
- Density: ASRS and mobile/shuttle systems concentrate pallets into a smaller footprint/volume than wide-aisle layouts, improving cubic utilisation and freeing up space for packing, staging, or growth.
- Energy (for cold chain): A smaller refrigerated envelope + fewer large doors opening + less forklift travel: typically reduces kWh per pallet; in some designs, aisle lighting loads also drop. Results vary by product and setpoints but the physics is consistent.
- Labour & accuracy: Automated put-away and retrieval reduce travel time and mispicks, stabilising service levels even with staffing variability.
- Safety & product quality: Less human handling means fewer impacts and shorter product exposure to ambient temperatures—critical for food and temperature-sensitive goods.
Indian regulatory & standards map (design with compliance in mind)
Designing for India means aligning your facility with sector-specific rules and general building & fire codes:
- Food & cold chain: FSSAI’s licensing regulations and hygiene standards (Schedule 4) require safe handling, segregation, cleanliness, pest control, and temperature control. Frozen foods are expected to be held at or below –18 °C; chilled setpoints should meet label or category requirements. Build your SOPs (monitoring, logging, alerts, calibration) around these baselines.
- Pharmaceuticals: CDSCO Good Distribution Practices (GDP) cover storage conditions, temperature mapping/monitoring, documentation, and traceability across the distribution chain—including warehouses and logistics partners.
-
Fire & life safety: The National Building Code of India (NBC 2016), Part 4 (Fire & Life Safety) sets the framework for industrial/storage occupancies—think compartmentation, exits, detectors, hydrants/sprinklers, and fire command features. Pair NBC requirements with your authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) and insurer conditions.
- Racking structural design: Rinac’s storage solutions reference EN 15512 (steel static storage—adjustable pallet racking). This is a recognised design basis for rack structures and a useful reference for reviewers/insurers.
- Fire-rated envelope: Where insurers or AHJs require enhanced fire performance, FM-Approved PIR panels (e.g., Firearmet) help align with loss-prevention criteria in cold stores and industrial shells. Match panel classes and assembly details to your hazard and insurer’s guidance.
Infographic (insert): “Compliance by design” checklist showing FSSAI Schedule 4 hygiene controls, GDP storage/traceability, NBC Part 4 fire systems, EN 15512 rack design basis, and FM-approved envelope options—mapped to each project phase (design, build, operate).
Source references: FSSAI, CDSCO GDP, NBC 2016, EN 15512, Rinac/Firearmet pages.
Choosing the right ASRS path with Rinac’s portfolio
Below is a practical fit-guide rooted in Indian use cases:
1) Multi-deep shuttle racking (high-density pallets)
Best for frozen commodities, dairy ingredients, edible oils, and large batch SKUs where LIFO/FIFO by lane is acceptable. Motorised shuttles carry pallets along deep channels; front-end lifts or reach equipment feed the system. ASRS layers can automate the sequencing.
Image (insert): Deep-lane shuttle racking perspective showing shuttle rails, shuttle dock, and front transfer zone.
Visual inspiration: Rinac gallery—multi-deep shuttle racking.
2) Unit-load crane ASRS (tall pallet aisles)
For pharma secondaries, high-mix FMCG, and 3PLs requiring structured locations, traceability, and high vertical reach. Pair with ambient or chilled rooms built from insulated panels (for temperature control) and with fire-rated assemblies where required.
3) Mobile racking (compact with a single movable aisle)
Ideal when you need density and frequent access across many SKUs—common in 3PL and food DCs. Mobile bases open one aisle at a time, drastically raising slot count in the same footprint; can be combined with guided picking or automation front-ends.
Image (insert): Mobile racking bay with carriage rails and control panel callouts; overlay showing aisle-opening logic and safety scanners.
4) Miniload or tote/carton ASRS
For high-value, small-format SKUs: nutraceuticals, cosmetics, spares. Great where pick accuracy and batch wave management matter.
5) Mezzanine-assisted storage
Multiply floor area for kitting/packing while keeping the ASRS core for pallet movement. Useful in ambient FMCG and e-grocery sortation.
Building envelope & interiors that support automation
Insulated PUF panels (InstaWall/InstaCeil/InstaRoof) deliver quick-to-install, modular shells with thermal performance and Class ‘O’ (BS 476 parts 6 & 7) / B2-grade fire-rated properties—as specified by Rinac—suited to building controlled spaces that stabilise ASRS performance (fewer defrost cycles, tighter temp swings).
For tougher fire-loss-prevention mandates, Firearmet FM-Approved PIR panels add high-temperature stability, closed-cell moisture resistance, and FM classes 4880/4881/4471 for walls/roofs. This is especially relevant for insurers covering automated cold and ambient storage with high rack heights and dense loads.
Cutaway (insert): “Cold-store wall section for ASRS”—showing panel skins, PIR/PUF core, vapour-tight joints, flashing, thermal break at base, and embedded rack footings separated from the cold envelope.
Source references: Rinac PUF & Firearmet pages.
A phased blueprint to implement ASRS with Rinac
Throughput & slotting study
- Quantify pallets in/pallets out, SKU velocity, temperature zones, and required service levels.
- Decide on shuttle vs. unit-load vs. mobile based on SKU profile and FIFO/LIFO needs.
Rack schema & standards
- Draft rack elevations to EN 15512 principles (beam loads, deflection, anchors, seismic where applicable).
- Include provisions for maintenance aisles, rescue, fire detection/suppression, and egress.
Envelope & MEP integration
- Define insulated envelopes (PUF/PIR), vapour barriers, door counts, dock locks/air curtains.
- For cold stores, target FSSAI-aligned SOPs: continuous temperature logging, calibrated probes, alarm/response.
Controls, WMS & traceability
- Integrate ASRS PLCs with WMS/ERP.
- For pharma: map GDP controls—quarantine locations, controlled returns, temperature excursions, audit trails.
Fire & life safety
- Coordinate sprinklers/deluges, detectors, in-rack lines where applicable; confirm NBC Part 4 compliance and AHJ approvals.
- Consider FM-Approved panels in high-risk zones; engineer compartmentation and smoke management
Commissioning & validation
- Temperature mapping (for cold rooms), load tests, controls FAT/SAT, SOPs, and staff training.
Infographic (insert):“ASRS project plan—24-step checklist from business case to go-live.”
Sections: data → concept → detailed design → build → commissioning → SOPs → continuous improvement.
India-specific use cases & design notes
Food & cold chain (frozen, chilled, and produce)
- Problem: power costs and product losses from temperature fluctuations.
- Design notes: deep-lane shuttle ASRS for batch SKUs; fast-cycling insulated doors; vestibule docks; vapour-tight panels; temperature & defrost SOPs; and density to shrink the cold envelope.
- Compliance: FSSAI Schedule 4 hygiene and sanitation, temperature control and records; frozen foods ≤ –18 °C; staff hygiene and pest control.
- Rinac fit: shuttle racking or mobile racking + PUF/PIR panels + optional FM-Approved Firearmet for fire performance.
Image (insert): Frozen room racks with evaporator units and aisle lighting—illustrating clear airflow paths and drip-free coils.
Visual inspiration: Rinac cold-room gallery.
Dairy and seafood
-
Problem: strong seasonality and batch sizes; strict cold chain.
-
Design notes: multi-deep systems for batch-in/batch-out; corrosion-aware finishes; wash-down friendly panels and floor detailing.
-
Rinac fit: StorEdge shuttle or drive-in + Rinac insulated envelopes proven across dairy/seafood segments.
Pharmaceuticals & nutraceuticals
-
Problem: strict storage conditions, audit trails, and segregation.
-
Design notes: miniload/tote ASRS or mobile racking in controlled rooms; validated temperature mapping, GDP documentation, quarantine zones, FEFO logic in WMS.
-
Compliance: CDSCO GDP guidelines for storage, monitoring, documentation, and distribution practices.
-
Rinac fit: StorEdge for pallets/totes; insulated partitions; Firearmet in high-risk zones; controlled docks and ante-rooms.
Operations: what to measure after go-live
-
Cubic utilisation (pallets/m³) and pallets per aisle-metre
-
Throughput: pallets in/out per hour; cycle times by SKU class
-
Order accuracy: % perfect orders; mispick rate
-
Energy intensity: kWh per pallet stored (or per tonne throughput), especially for cold stores
-
Quality & safety: temperature excursions, pick damage, near-miss/safety observations
-
Maintenance: MTBF/MTTR for ASRS equipment; planned vs. unplanned downtime
Mini-chart (insert): KPI dashboard mock-up showing density and kWh/pallet trending down post-ASRS.
FAQ (India context)
Q1: Can ASRS work in very low temperatures?
Yes—ASRS is widely deployed in frozen facilities. Benefits include reduced door openings and less forklift traffic inside the cold zone—factors that help stabilise temperatures. Engineering choices (lubricants, heaters for rails/controls, defrost strategies) must match your setpoints.
Q2: Will regulators accept automated systems for food/pharma?
Automation is not a hurdle if hygiene, temperature, segregation, documentation, and traceability are in place. For food, align SOPs and records to FSSAI; for pharma, map flows to CDSCO GDP. For safety, meet NBC Part 4 and AHJ/insurer requirements.
Q3: What standards apply to racks?
Rinac racks follow EN 15512 principles (steel static storage systems for adjustable pallet racking), a recognised design basis that addresses structural reliability under typical load cases.
Q4: What about the building shell and fire performance?
Use insulated PUF/PIR panels for thermal performance and quick installation; in higher fire-risk or insurer-driven cases, Firearmet FM-Approved panels provide additional assurance (FM Classes 4880/4881/4471).
Putting it all together: a Rinac-ready ASRS stack for India
-
Storage core: StorEdge ASRS with the right mix of shuttle/multi-deep, mobile, and selective zones—engineered to EN 15512.
-
Envelope: PUF/PIR insulated rooms and partitions for ambient/chilled/frozen zones; option for Firearmet FM-Approved panels in high-exposure occupancies.
-
Compliance: SOPs aligned to FSSAI (food) and CDSCO GDP (pharma), and NBC Part 4 fire & life safety.
Call-to-action: If you’re planning a greenfield cold store, a pharma DC, or a brownfield density upgrade, a joint workshop with your operations, QA/Regulatory, insurance/AHJ, and Rinac’s engineering team can translate this blueprint into a site-specific concept—complete with energy and throughput modelling, compliance checkpoints, and a phased migration plan.
Credits & references
-
Rinac Warehouse Storage & Racking Solutions / StorEdge overview (EN 15512 design; ASRS, shuttle, mobile, mezzanine).
-
Rinac Firearmet FM-Approved panels (FM 4880/4881/4471; EN 14509/ISO quality).
-
Rinac PUF sandwich panels (InstaWall/Instaceil/InstaRoof; Class ‘O’ per BS 476 parts 6 & 7; B2 fire-rated PUF).
-
Rinac blogs on cold storage, racking, and shuttle systems.
-
FSSAI licensing & hygiene (Schedule 4) and storage temperatures (e.g., frozen foods at or below –18 °C).
-
CDSCO Good Distribution Practices (GDP) for pharmaceuticals (storage, monitoring, documentation).
-
NBC 2016 Part 4 (Fire & Life Safety) for industrial/storage buildings.
-
Independent coverage on ASRS benefits in cold storage (density & energy context).
-
EN 15512 references (rack structural design principles).